Medial Branch Block
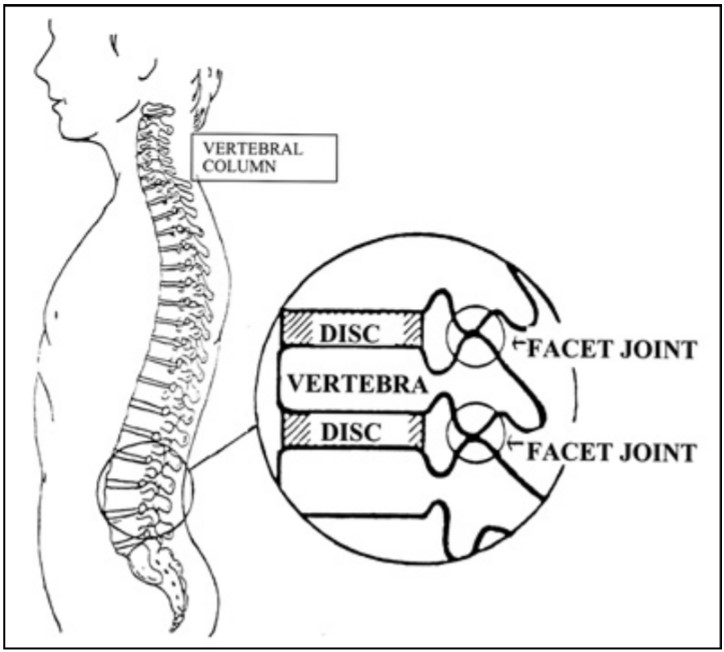
What is a Facet Joint?
The facet joints are located at the back of the spine on both sides where one vertebra overlaps the next. The facet joints provide stability and give the spine the ability to bend and twist. The joints are surrounded by a joint capsule, which contains lubricating liquid.
What is a Diagnostic Facet joint nerve block (diagnostic medial branch blocks)?
Facet joint nerve blocks involve temporarily numbing the nerve supply of the facet joints and adjoining soft tissues. The procedure is a test (diagnostic) to see if you get any short term pain relief from it. Your doctor could then discuss the further plan of pain management following the procedure.
How does it work?
The injectate is a local anaesthetic. Local anaesthetics numb the nerves supplying the facet joint, giving short-term pain relief, but only if your pain is predominantly mediated by the structures involving these nerves.
How is it done?
This procedure is performed as a day case procedure. The risks and benefits will be discussed with you in the outpatients department and a consent form completed. You will be admitted to the day ward and seen by one of the pain doctors who will ask you if you have any further questions about the procedure, and mark the skin. You would be provided with a diagnostic pain injection diary, this is a very important document to assess the results of this procedure, hence please keep this safely and bring it to your follow up appointment with the doctor. The doctor, or the staff, will explain to you how to fill this diary. Shortly before the procedure you will need to change into a hospital gown.
For this procedure you will lie on your tummy on an operating table. Some patients may require a plastic cannula (needle) to be placed in the back of the hand. We will monitor your breathing and circulation. You will remain awake for this procedure. Your lower back will be cleaned with a cold antiseptic solution. This procedure is performed using X-rays to ensure that the needles are in the right position. Local anaesthetic may be injected into the skin to numb the area. There may be some discomfort in the back at the time of the procedure. This procedure could involve placing multiple needles. A small dressing will be applied at the site of injection, which can be removed after 24 hours. Do not worry if it falls off sooner.
After the procedure, it’s very important that you fill in the pain diary at regular intervals as suggested. We suggest that you maintain your usual activities on the day of the procedure, and attempt to do something that would normally bring on your usual pain. On the pain injection diary, you could document your pain levels before and after the injection. We also suggest that you make some notes on the diary to help you recall in detail about your activities and your pain post-procedure on the day of the procedure, this could help your doctor better interpret the results of this test procedure.
What are the common side effects?
You may have increased pain for few days following the procedure. This usually improves.
You may feel numbness or reduced sensation in the arm or the leg after the procedure, this settles after a few hours.
If this procedure relieves your pain, please remember that it is only a test and not a cure. It is usual for pain to return at variable time interval after this injection.
Who do I contact if I am concerned after the injection?
You can contact the Walton Centre during normal working hours (Monday to Friday), on 0151 525 3611, and ask to speak to the secretary of the doctor who did the procedure.
Out of these hours, or at weekends, please contact your emergency GP or Urgent Care centre.
If you have any questions, then please contact your pain consultant before the procedure.
- Last Updated:01 July 2022
- Review Date:01 July 2024
- Author:Dr M L Sharma
- Summary:
Facet joint nerve block involves temporarily numbing the nerve supply of the facet joint and adjoining soft tissue.